Do you need a stencil? An insulation sheet? A seal or protective cover? Or a flexible lampshade? In short, a foil, cut according to your own design? In this blog, you can read which foils you can have laser cut and which are suitable for your application.
What is a foil?
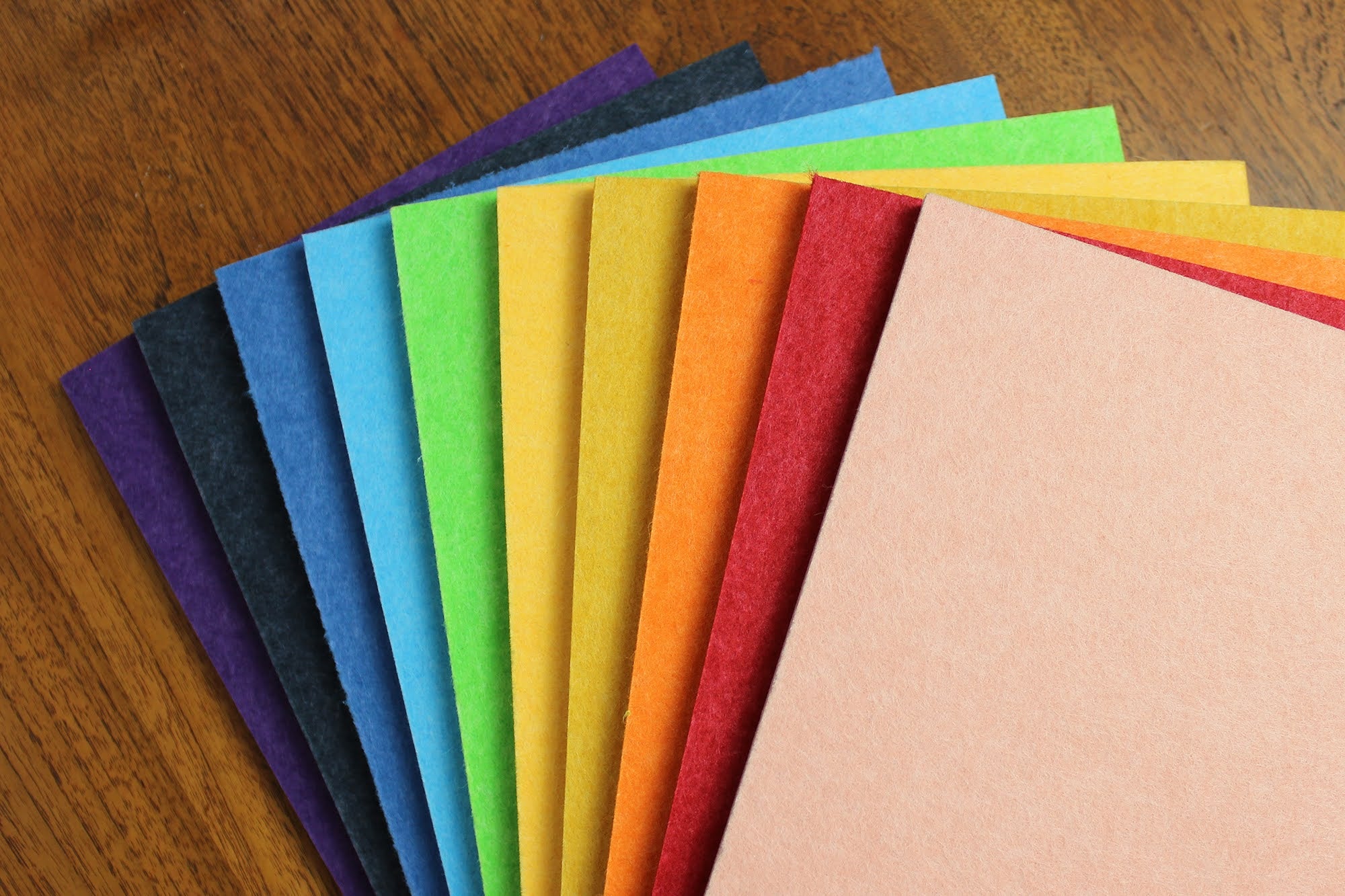
We're talking about thin plastics (100 microns to about 1mm) and other "nonmetals" that you can easily bend and sometimes fold without breaking. Flexibility varies by material but depends mostly on thickness. The thinner a material, the easier you can bend it. Therefore, as long as they are very thin, you can sometimes consider rigid materials such as acrylic as films.
Why laser cut foil?
With laser cutting, you can make small details and complex shapes have them cut into foils. The start-up costs are low so it is also interesting for prototyping and one-off projects. The cutting width of the laser is about 0.1mm so you can sharp corners can be made. Because laser cutting is a non-contact technique, no force is applied to the film during the cutting process. As a result small details of your design remain intact. Finally, there is a minimum "heat affected zone" (the stretch along the edge where the material is affected by the laser). That is, the edges remain neat and strong. All in all, this makes it perfectly possible to make details on the order of 1mm and sometimes less.
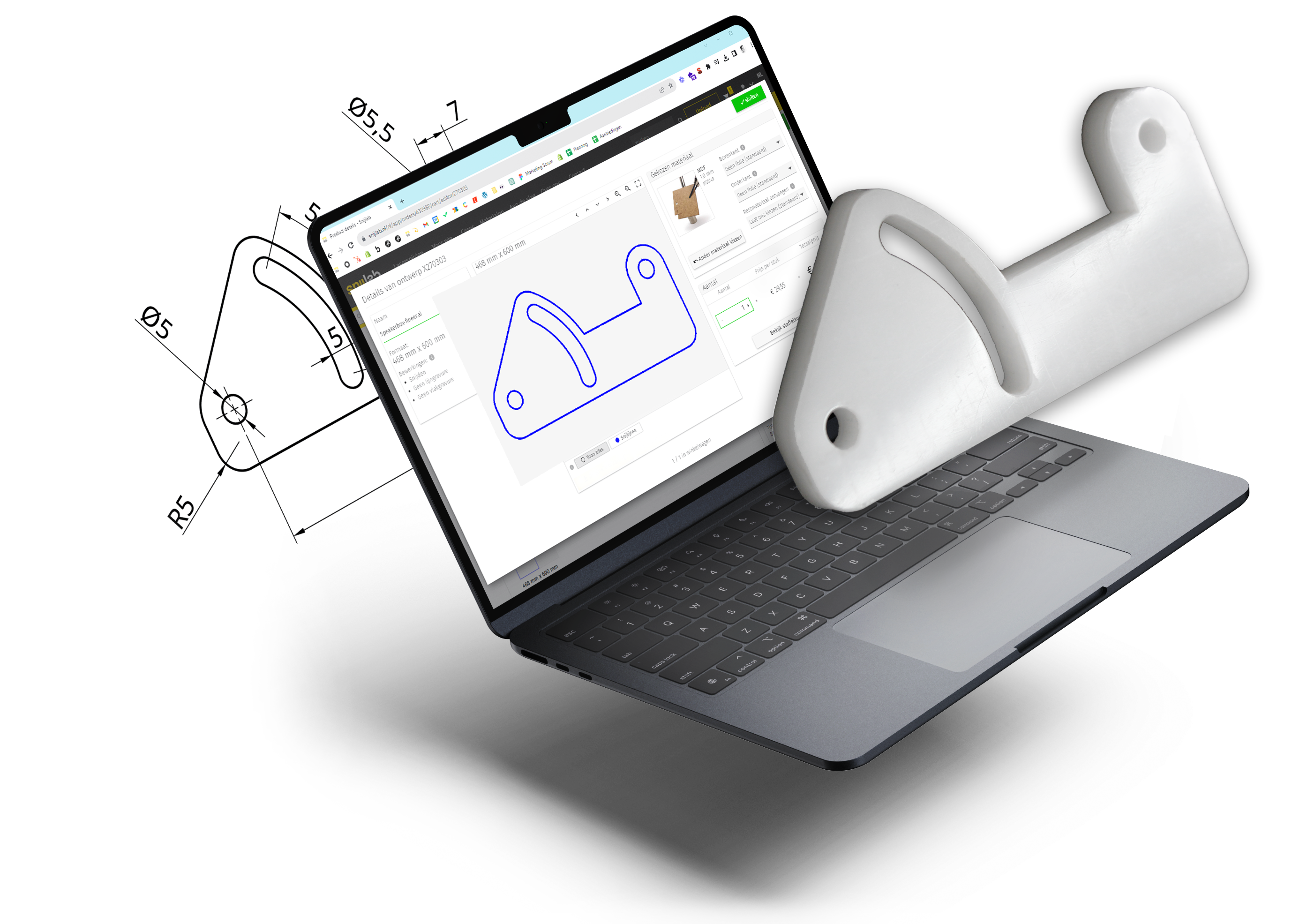
Laser cutting a film according to your design is very simple. With your digital design, you can request a price from us in just a few clicks and, if desired, order online. So you never have to wait for a quote and you can quickly see what design adjustments will do to the price. When you're ready to order, you can do it yourself online.

What does it cost to have a foil laser cut?
TLDR; from about €20 you will have a custom laser cut film in your home. In quantities, the price can drop to €0.05 per part.
The price for laser cutting consists of:
- Price per m² of material - Usually the cost of materials is a small factor in the price. Material costs do become important if your design is large (>200x200mm) or if it is serial work.
- Processing costs - The cost of the actual lasering depends mainly on the total length of cutting lines. For serial work or complex designs (e.g., a stencil with a large hole pattern), this can be the most important factor in the price.
- Start-up costs - these are between €10 and €20 depending on the material. For single pieces and prototyping, this is often the biggest factor in the total price. It therefore pays to include several test pieces or designs in one order.
- Shipping costs - From € 6.50 within the Netherlands.
The best way to find out the price for your design is to make a (mockup) drawing. upload. You'll see the price immediately and you can also compare materials. Uploading is free and you are not stuck with anything.
As a rule, single pieces, prototypes and small projects of laser-cut foils thus come out at €20-€50 depending on the size.
Series prices vary, but small foil parts can be ordered (in runs of several hundred or thousands) for as little as €0.05.
This makes laser cutting of foils ideal for projects, research and prototypes. And also for products that are frequently modified, because with laser cutting you are not stuck with a mold or die.
Laser cutting films in series
Larger runs or serial work involve more than a prototype. After all, everything must be correct and remain correct; tolerances, quality of finish, but often also packaging and the delivery schedule.
We see more and more customers with a production demand choosing to produce serial work in smaller quantities, and preferably close by, as opposed to mass production in low-wage countries. On the one hand, this is made possible by increasingly inexpensive digital production techniques such as laser cutting and 3D printing. On the other hand, it offers advantages because, as a customer less risk run, can switch more easily between manufacturers, and more frequent adjustments in your design.
To further increase quality and consistency of laser cutting in series, we have a special production line for serial work developed. This allows us to offer even higher quality at low cost.
When is it better to punch?
Die-cutting is a technique in which a die-cutting jig is used to cut and sometimes shape materials.
To die-cut, a die-cutting jig must first be made. This creates a one-time high start-up cost. Also, you cannot make as small details with die-cutting.
A big advantage of die-cutting is that once the mold is paid for, the cost per part is very low. This makes it ideally suited for mass production. Die-cutting is therefore the best choice for projects with very large runs. But also when, for example, materials are needed that contain toxic components such as PVC, and with thermosets such as polycarbonate that cannot be laser cut properly or safely.
In short, die-cutting is especially a good option for out-of-print, high-volume designs.
What do you use laser-cut films for?
Foils are used by our customers in engineering, product design, and remarkably in the renewable energy sector. But you can also do a lot with foils in creative projects, hobby and education. In industry, for example, foils are used as cell separators, acting as an insulating layer between cells in battery systems to prevent short circuits. Or they are used to make seals and gaskets, which provide an airtight seal or fill spaces in various mechanical and industrial applications.
There are also many films with which you can make good stencils. Lasered stencils can be enormously detailed and complex.
Plastic film membranes are used for filtration, separation and protection of various materials and systems. In addition, films serve as protective layers in devices, where they protect sensitive components from damage and external influences.
Finally, the materials below are also used as protective hoods and windows, where they serve as transparent and protective layers for various products and systems.
What films are there and what are the differences?
Acetate film
A thin, strong and transparent film with good insulating properties.
We have this film in 100, 250 and 500 micron thicknesses making it the thinnest film you can have laser cut. Due to the small thickness tolerance, this film lends itself to filling spaces, for example. But also as a protective layer and as an insulation sheet. The laser cut is neat and there is little melting along the edge. As a result, very small details in the order of 1mm are possible. You can therefore also use this material very well for detailed stencils.
Polypropylene foil
This is a flexible and tough plastic that can be bent easily. It has a textured surface on one side that makes it scratch resistant (you won't see scratches because of the texture). This makes laser-cut polypropylene film ideal for products that are often touched and seen. For example, it is used as a faceplate for appliances, installations in public spaces, but also sometimes as an intermediate layer of insulation in appliances. PP is relatively inexpensive.
The cutting edges can have a small melting edge of 0.1-0.2mm. If you want it completely without a melting edge, then choose laser cutting with protective film. If you have it cut without protective film, you can easily wipe off any laser marks with a damp cloth.
PP film is available in white and black at 0.8 and 1.2mm thickness.
PETG or polyester film
Polyester is transparent and impact-resistant. It is also inexpensive, strong and flexible. The windows of our splash screens for example, are made of polyester. In model making, it is used for windows, although precision acrylic is actually a better choice for that. Lasered polyester comes standard with protective film on two sides. You can make reasonably small details in it, but pieces that are too thin can warp when cut. If you fold polyester along a ruler (aka "cold forming") it will stay in position. So with that, you can easily make 3D shapes. One disadvantage of polyester is that it is relatively soft and therefore prone to scratching.
Polystyrene
Thin polystyrene is flexible and soft. It has a matte surface. It is fine to cut by hand and easy to glue. This makes it suitable for model making and maquette work.
A disadvantage is that it is somewhat weaker and stains are difficult to remove.
POM
POM. In a word; Strong. POM is a high-quality plastic and one of our best sellers. It can be considered flexible, but it is considerably stiffer (less pliable) than polypropylene, for example. Its surface is smooth and has a slightly waxy feel. With excellent sliding properties and wear resistance, POM is a solution for many mechanical applications. It is, however, a more expensive option than pp, for example. It is difficult to glue POM (but double-sided adhesive film will work). Cutting with a Stanley knife is also not possible.
Precision acrylic
Actually, precision acrylate does not fall under the category of films, but it is an excellent choice if you need a super smooth surface, small details and a transparent material. Compared to PETG, you can make much smaller details in precision acrylate. Dates or slots of a millimeter or smaller are perfectly possible. It is crystal clear, UV resistant and comes with protective film on both sides. However, be careful because acrylic is fragile, especially with small details. It can also scratch easily, so treatment with care is required. The thickness tolerance of precision acrylic is better than that of regular acrylic.
Laserboard
Finally, we would like to name one more special material: Laserboard. It is a composite material of paper soaked in resin. This makes it waterproof, strong and flexible. What distinguishes laserboard from plastics is that it does not deform or melt when heated. This means that you can laser cut even the tiniest details (such as hole grids with only a few tenths of millimeters between them) in laser board without it deforming due to heat. The surface has a slightly fibrous texture.
Double-sided adhesive film
You can optionally have this foil applied to your laser cutting to make it self-adhesive. But did you know that you can also have it laser cut separately?
It is a very thin, semi-transparent plastic film with high adhesive strength. You receive it flat, with a paper protective layer on both sides. So you can easily apply it to your own products or parts.
Perhaps also interesting:
Still laser cutting a different film?
We have a lot of experience with laser cutting foils and can in some cases order specialty foils for you, or you can provide them yourself to have them laser cut. In that case, please contact contact us. A few examples are:
- 3M film laser cutting
- Mylar film laser cutting
- Other colors and thicknesses PP film laser cutting
- Laser cutting of polycarbonate film
- Laser cutting of polyamide film
Have questions or want to discuss the best choice for your application? Please contact contact and we will be happy to help you!